What is a random integer? Is an integer choosen randomly between 1 and 1000000 really representative for all
integers choosen randomly? We can see that our experience is only an approximation of an ideal model. Here, we’re
going to modify the method for generating random integers... We won’t use the primitive random, we’re going to
generate random integers with the π digits sequence.
π digits have always interested mathematicians:
- The numbers 0 to 9, do some appear more often than others?
- Is there some sequence of integers that appear frequently?
In reality, it seems that the π digit sequence is a really randomly sequence. (Result not demonstrated yet). It’s not
possible to predict the following digit after the others, there’s no period.
Here is the method we’re going to use to generate integers randomly choosen:
Let’s create now a new procedure called randompi and let’s modify the procedure test
to gcd :a :b
if (modulo :a :b)=0 [output :b][output gcd :b modulo :a :b]
end
to test :tries
# We open a flow whose identifier is 1 towards the file millionpi.txt
# Here we suppose that millionpi.txt is in the current directory
# Otherwise, fix it with changedirectory
openflow 1 "millionpi.txt
# Set the variable line to the first line of the file millionpi.text
globalmake "line first readlineflow 1
# Set the variable counter to 0
globalmake "counter 0
repeat :tries [
if 1=gcd randompi 7 randompi 7 [globalmake "counter :counter+1]
]
# Calculate frequency
globalmake "f :counter/:tries
# Display th pi approximation
print sentence [ pi approximation:] squareroot (6/:f)
closeflow 1
end
to randompi :n
localmake "number "
repeat :n [
# If there’s no char yet on the line
if 0=count :line [globalmake "line first readlineflow 1]
# Set the variable char to the first character of the line
globalmake "char first :line
# Then remove first character from the line.
globalmake "line butfirst :line
globalmake "number word :number :char
]
output :number
end
test 10
approximation de pi: 3.4641016151377544
test 100
approximation de pi: 3.1108550841912757
test 1000
approximation de pi: 3.081180112566604
test 10000
approximation de pi: 3.1403714651066386
test 70000
approximation de pi: 3.1361767950325627
|
We find a correct approximation of π with its own digits!
It’s still possible to imrove the program by indicating the time for the computation. We add on the first line of the
procedure test:
globalmake "begin pasttime |
Then we append before closeflow:
print sentence [pasttime mis: ] pasttime - :begin |
 First number
First number 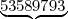 Second number
Second number 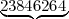 Third number338327950288419716939
etc
Third number338327950288419716939
etc